Allergy Diagnostics
Accurate diagnosis is the key to fighting off an allergy because avoidance of the allergen is the best way to treat it. The allergy diagnostics begins with the gathering of the patient’s medical history: doctor asks questions about symptoms, their origin and progress, family history of allergy, nature of their work, coexisting diseases, and drugs that they may take. When the patient keeps a symptom diary, it can be very helpful in arriving at a diagnosis. On top of a physical exam, medical testing may include additional methods, such as a lung function test. Skin and blood tests are used to detect the presence of antigen-specific immunoglobulin E.
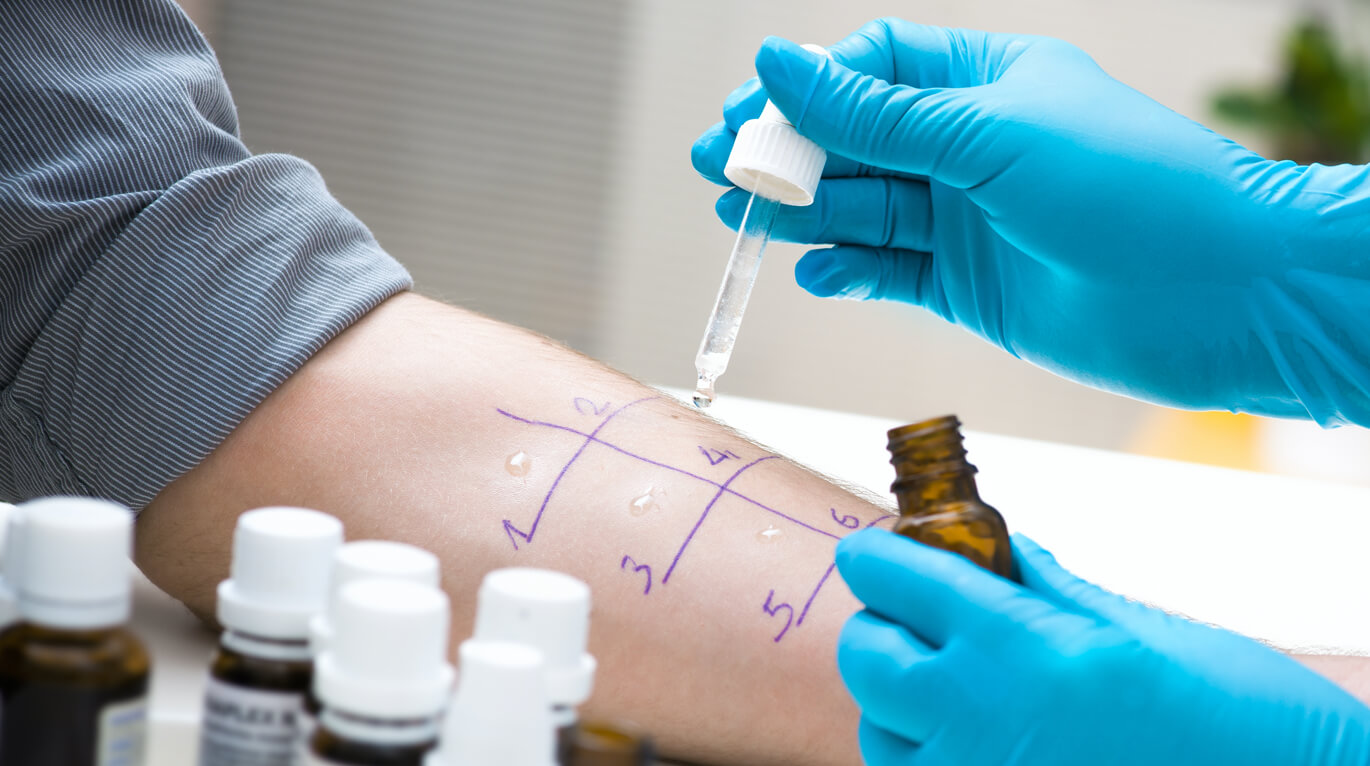
Skin Test
Skin allergy testing is carried out by applying a small number of suspected allergens or their extracts on the skin surface and marking the test areas with a pen. Tiny scratches (scarification test) or pricks (prick test) are made in these areas. Sometimes allergens can be injected under the dermis with a syringe but the principle is basically the same. The skin test is usually done on the back or inner forearm.
If the test site becomes inflamed within an hour after exposure to an allergen, the result is positive. The severity of allergic reactions may vary depending on the sensitivity: from reddish skin to a papule looking like a florid mosquito bite. The skin test is then scored on a special scale by an allergist.
Patch tests are used to detect allergic contact dermatitis. Various allergens are applied to patches, which are then placed on a patient’s skin. It takes at least two times to interpret the results: 48 hours and 2-3 days later after the test.
Blood Analysis
Detecting and measuring the number of specific antibodies in blood has a lot of pros. There are practically no contraindications for allergy blood tests, and one blood sample is enough to check you for a great number of antigens. Unlike skin testing, blood tests can not trigger anaphylaxis, are not contraindicated for patients with skin diseases or those treated with antihistamines.
Challenge Tests
A small amount of allergen is applied in a way that allows the substance to immediately reach the organ, where the patient has allergic complaints, i.e. taken by mouth, inhaled or otherwise. It requires the supervision of an allergist and is used to diagnose drug or food allergies.
Elimination Tests
A patient is instructed to avoid the particular allergen for some time. Once the allergic symptoms are relieved, the allergen is put back and body reaction is monitored.