Trichomoniasis (Trich): Causes and Symptoms
Disclaimer: Not medical or professional advice. Always seek the advice of your physician.
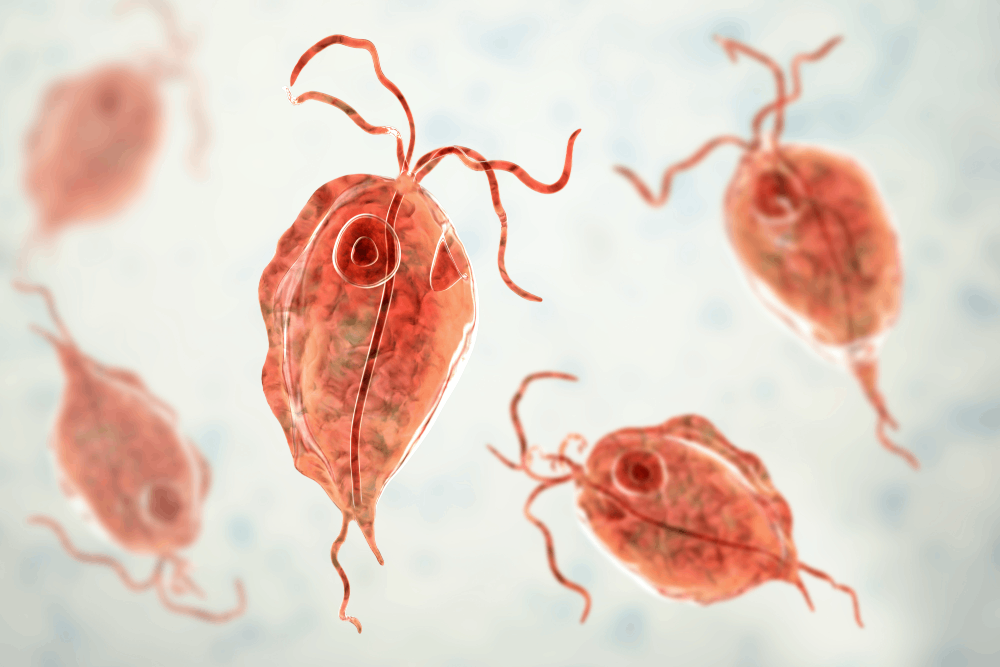
Trichomoniasis (Trich) is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the protozoan Trichomonas vaginalis. The infection does not go away on its own, so it must be treated. The WHO estimates an incidence of around 250 million cases of trichomoniasis each year. Women are more likely than men to get the disease.
Trichomonas vaginalis, a single-celled protozoan parasite, is the etiologic agent of trichomoniasis. It can move with the aid of flagella.
When was Trichomoniasis First Diagnosed?
- Alfred Francois Donné, a professor of microscopy at the Collège de France, while examining women’s vaginal discharge, discovered Trichomonas vaginalis almost 180 years ago. Moreover, studies have found that Trichomonas vaginalis can coexist with syphilis and gonorrhea in one organism.
- Two years later, the German zoologist Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg classified T. vaginalis as the ciliated protozoa. However, further research had been stopped. Ehrenberg believed that T. vaginalis (like most ciliates) is relatively harmless.
- 35 years later, the Russian obstetrician Lazarevich Ivan Pavlovich noticed that T. vaginalis is most frequently detected in women experiencing inflammation of the genital tract.
- The pathogenicity of Trichomonas was confirmed before World War II. Then scientists spent the following two decades trying to identify the transmission route of the infection.
How do People get Trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis spreads between men and women through vaginal sex. Women can spread T. vaginalis to other women through sexual contact. Men do not usually get the infection from other men. Trichomoniasis is not thought to be passed on through oral sex. T. vaginalis is not resistant to sunlight and hot water and immediately dies from any antiseptic.
Trichomoniasis Symptoms

Most infected people have an asymptomatic course of trichomoniasis. According to some sources, 70%–80% of patients have minimal or no genital symptoms. Signs and symptoms of infection may appear 5-28 days after exposure.
Common Symptoms of Trichomoniasis in Men and Women
- genital itching or irritation
- redness in the genital area
- burning sensation when urinating
- discomfort during intercourse and urination
- lower abdominal pain (in rare cases)
Symptoms of Trichomoniasis in Women
- frothy vaginal discharge (usually yellow or green) with an unusual, foul odor
- inflammation and redness of the vulva
- sores in the mucous membrane of the vagina
Symptoms of Trichomoniasis in Men
- mucus-like urethral discharge
- hematospermia, the presence of blood in the semen (in rare cases)
- rash on the glans (head of the penis)
What Makes Trichomoniasis Dangerous?
- It increases the risk of transmission and acquisition of HIV (by 3-4 times, according to experts).
- Adverse outcomes of pregnancy (preterm delivery and low birth weight).
- Men can develop prostate cancer due to asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis or urethritis.
- Individuals infected with trichomonas vaginalis have a higher risk of cervical cancer, especially those co-infected with high-risk oncogenic HPV.
Trichomoniasis and HIV
Trichomonas vaginalis infection is associated with a significantly increased risk of becoming infected with HIV. Statistics show that up to 53% of women with HIV infection are also infected with T. vaginalis. Moreover, trichomoniasis is known to cause pelvic inflammatory diseases.
There are several reasons why trichomoniasis can raise the risk of getting HIV.
- Trichomoniasis causes tiny areas of bleeding within mucous membranes that provide a pathway for HIV infection.
- The Trichomonas vaginalis parasite breaks down an enzyme that blocks HIV attachment to cells.
Trichomoniasis and Pregnancy
Trichomoniasis in pregnancy may be associated with an increased risk of preterm birth (before 37 weeks of gestation) and low birth weight. Preterm or low-birthweight babies have a higher risk of health and developmental problems at birth and later in life. Perinatal transmission of trichomoniasis occurs rarely, but pregnant women still need treatment. It will help prevent respiratory or genital infections in newborns.
How is Trichomoniasis Prevented?

- Use condoms. Condoms are the best way to prevent STIs during sex. It is very important that condoms are put on before any sexual contact occurs between the penis, vagina, mouth, or anus. Contraction and transmission of trich can occur without ejaculation. Other methods of birth control, like birth control pills, shots, implants, or diaphragms, will not protect against STIs.
- Get tested. Make sure your partner is also tested for STIs before having sex.
- Practice monogamy.
- Limit your number of sexual partners. STI risk increases with the number of sexual partners.
If you are exposed to trichomoniasis, you should get tested for other STIs, since they could be transmitted at the same time as trich.
