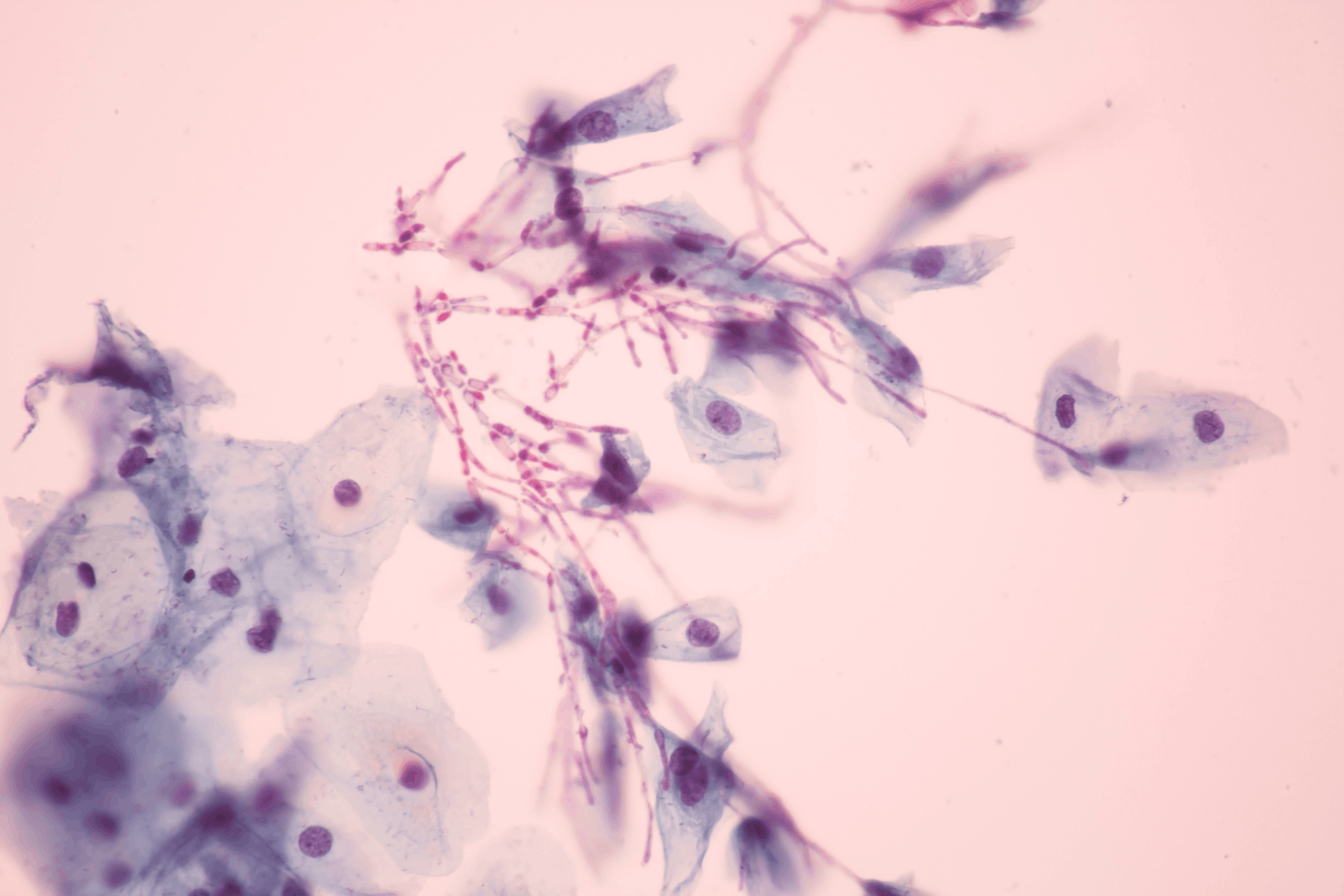
Causes and Symptoms of Candidiasis (Yeast Infections) in Women
Vaginal candidiasis is an infection caused by a type of fungus called Candida. It is one of the most prevalent diseases in the U.S. adult population. It should also be noted that candidiasis can occur in women who are not sexually active.
Both men and women can transmit this infection. Candida fungi normally live in the human body without causing any symptoms.
Common Causes of Yeast Infections in Women
In most cases, women do not even know the exact causes of the infection. But whatever triggers thrush, it always indicates a malfunction in the immune system. As the disease gradually weakens the body's natural defenses, good vaginal bacteria die off and the candida fungus gets a chance to grow unchecked. Therefore, candidiasis can become a warning sign of an infection in the body.
Apart from problems related to the immune system, a number of factors make thrush one of the most common gynecological diseases.
- thyroid disorders
- long-term use of medications
- weakened immune system
- hormonal imbalance
- diabetes mellitus
- STD
- pregnancy and breastfeeding
- chronic stress
- obesity or underweight
- poor hygiene
- infrequent changing of pads, tampons
- wearing synthetic underwear
Symptoms of Candidiasis in Women
The main symptom of the disease is intense burning and itching around the vulva and vagina. Other common manifestations of the infection include.
- white, sour-smelling, lumpy discharge
- redness of the labia minora
- swelling of the labia majora and labia minora
- pain during sex
- painful urination
Sometimes patients may have only one or more of the mentioned signs. Moreover, mild symptoms can occasionally go away without treatment and come back within a year (chronic candidiasis).
Diagnosis of Vaginal Candidiasis
The laboratory evaluation includes a microscopic examination of a vaginal swab. Additionally, the patient might need to have a blood test to identify other disorders in the body that could provoke candidiasis.
Sex and Yeast Infections
It is best to abstain from sexual intercourse after the appearance of the first symptoms of candidiasis, even if you plan to use a condom. Most physicians do not recommend having sex until the infection has cleared up. There are several reasons for this.
- Candidiasis leads to the formation of cracks and tiny fissures in the vaginal mucosa. Friction from sex can cause more irritation and pain in these areas, making it harder to heal.
- Some medicines for candidiasis contain oil, which can cause condoms to break. In general, contracting candidiasis through sexual activity is very unlikely. However, if a condom breaks, a woman is at increased risk of getting pregnant.
Common Myths about Candidiasis
Myth #1: Eating yeast-baked goods, foods containing starch and sugar can cause candidiasis.
There are two different types of yeast associated with vaginal candidiasis and puffy bread. Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a safe type of yeast used in baking. The causative agent of thrush is Candida albicans or Candida non-albicans. There is no evidence that high amounts of starch and sweets in a diet cause candidiasis. However, if you reduce the amount of sweet and starchy foods, it could only benefit you. Studies show that cutting off sugar in chronic candidiasis helps reduce the risk of its recurrence.
Myth #2: Probiotics Treat Candidiasis
Thrush cannot be treated with probiotic products. But in the near future, we might get a cure for this delicate problem. In 2000, a number of pharmaceutical companies started working on a vaccine against candidiasis. The main principle is based on the study of the immune response against fungal pathogens.
Myth #3: Sexual Partners Must also be Treated
Recent research shows that thrush is not an STD and is very rarely passed on through sexual contact. Therefore, the physician can prescribe treatment for the partner only if he has such complaints, as itching and burning, white or gray patches, and atypical discharge. If there are no symptoms, the healthy partner does not need local or systemic antifungal medications.